THE EVOLUTION OF CONSUMPTION MODELS
In the last decades, consumption models have changed and shifted from products to services; market trends focused on the importance of roots and authenticity.
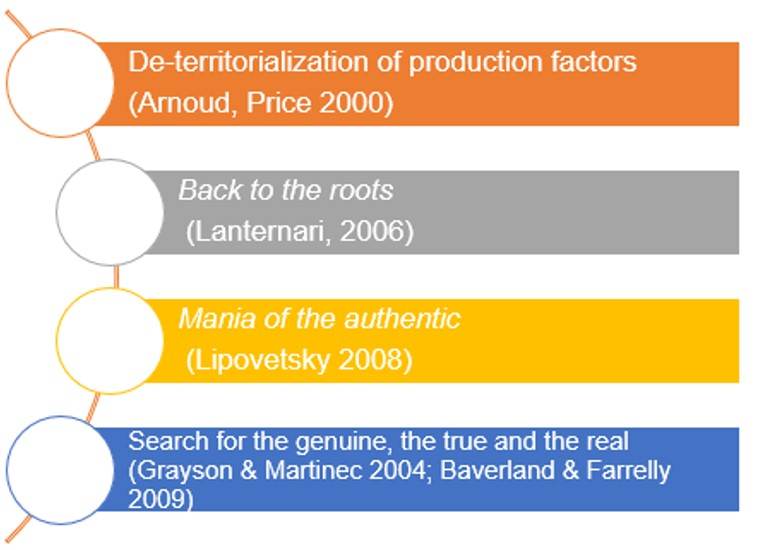
THE ROLE OF THE EXPERIENCE AND THE IMPORTANCE OF COMPETITIVE ADVANTEGES
In order to face these emerging trends, many enterprises reacted by giving progressive attention to the role of consumers in the value creation and by providing services focused on the experience and on competitive advantages represented by immaterial resources (Napolitano et al., 2018).

THE NATION BRANDING 1 / 2
The concept of “nation branding” was proposed by the American researcher Simon Anholt, who showed that a strong identity and a positive reputation create added value for competitiveness of a territory, contributing to the activation of a virtuous development (Anholt, 2007).
According to the Nation Brand Hexagon model (Anholt, 2000), the dimensions of nation brand are 6 and concern: tourism, exports, governance, investment and immigrations, culture and heritage, and people

THE NATION BRANDING 2 / 2
COUNTRY BRAND INDEX (CBI)
TOP 20 COUNTRIES

(Future Brand 2014-2015)
OVERALL BRAND RANKING 2013
TOP 10 OF 50 NATIONS
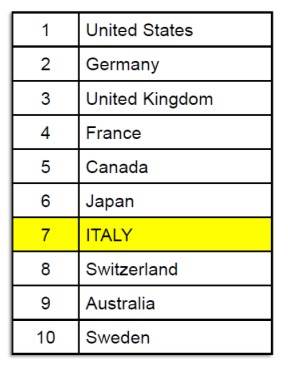
(Eurisko 2014)
WHICH IS THE VALUE OF “MADE IN”?
RANKING ACROSS INDUSTRY SECTORS
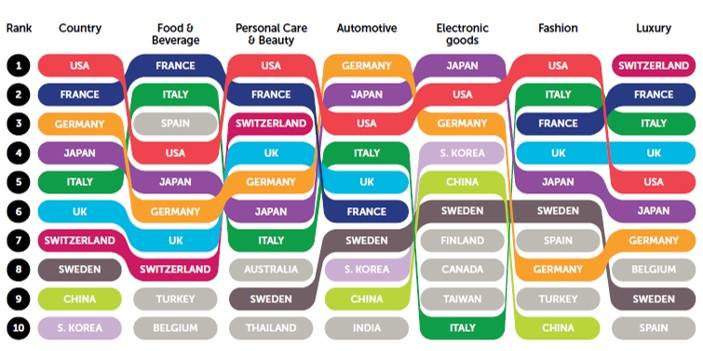
- Authenticity
- Expertise
- Differentiation
- Quality standards
THE QUALITY OF THE «ITALIAN WAY»…
The key element of the image and attractiveness of Italy abroad is represented by the quality of the «Italian way», who can be described through 6 dimensions:
- Landscape
- Tangible and intangible cultural heritage
- Made in Italy products
- Gastronomy
- Style, creativity and elegance
- Warmth and friendliness of Italian people
(Eurisko, 2014)
…AND THE NEW IDEA OF CULTURAL HERITAGE 1/2
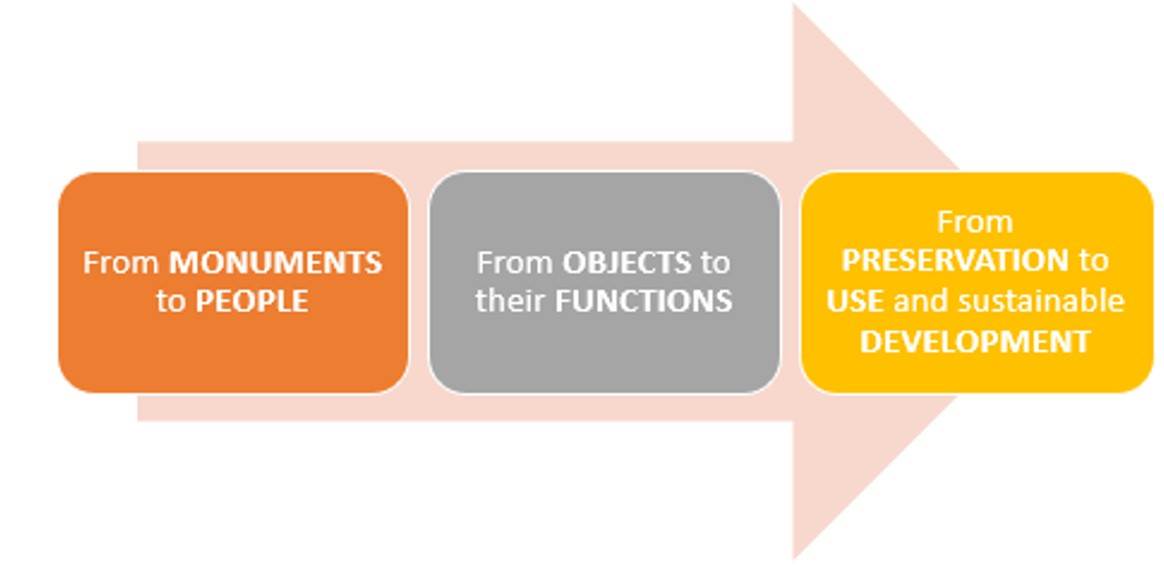
A more dynamic, open and inclusive conception of cultural heritage, including traditions, customs and local products.
…AND THE NEW IDEA OF CULTURAL HERITAGE 2/2
Cultural heritage is a group of resources inherited from the past which people identify […] as a reflection and expression of their constantly evolving values, beliefs, knowledge and traditions. It includes all aspects of the environment resulting from the interaction between people and places through time.
A heritage community consists of people who value specific aspects of cultural heritage which they wish, within the framework of public action, to sustain and transmit to future generations.
Council of Europe Framework Convention on the Value of Cultural Heritage for Society – Faro, 2005, art. 2.

CORPORATE HERITAGE AND HERITAGE MARKETING 1 / 2
Starting from these premises, the corporate heritage represents an asset to be enhanced, in order to promote both the company and the territory where the company activities are located.
In fact, besides creating products or services, companies must have an active and transforming presence on the territory, since they are amalgamated with and rooted in a specific environment, assuming an integrated identity between a certain community and its relational space, or rather, the identity of the territorial resources.
The firm may also have the physical or cultural characteristics of a certain place, arousing interest and curiosity in a target group and therefore assuming the identity of a tourist resource.
CORPORATE HERITAGE AND HERITAGE MARKETING 2 / 2
In this context, heritage must be seen as a resource.
It is the tangible sign of a specific territorial area and the union between the past and present, a collection of meanings, traditions, behaviors and attitudes necessary to understand the present, or rather to ensure continuity between the past and present.
Corporate heritage, as a dimension of corporate identity, is based on values and beliefs that historically characterised the company and allows to produce new languages able to strengthen the relationship with consumers.
To develop all these aspects and improve the linkages with external stakeholders, companies can adopt heritage marketing tools.
