Possible solutions for the elimination of fungicide residues in wine:
- Selection of the location of the vineyard after a thorough study in order to avoid fungal diseases.
- Effective vineyard management in order to minimize fungal diseases (eg. efficient bunch aeration)
- Good Agricultural Practices (GAP), i.e. correct fungicide dose and/or pre-harvest safety interval.
You could find more about Good Agricultural Practices on fruits here: http://www.fao.org/3/a-i6677e.pdf
- Use of protecting clothing and safe techniques for spraying by vineyard workers
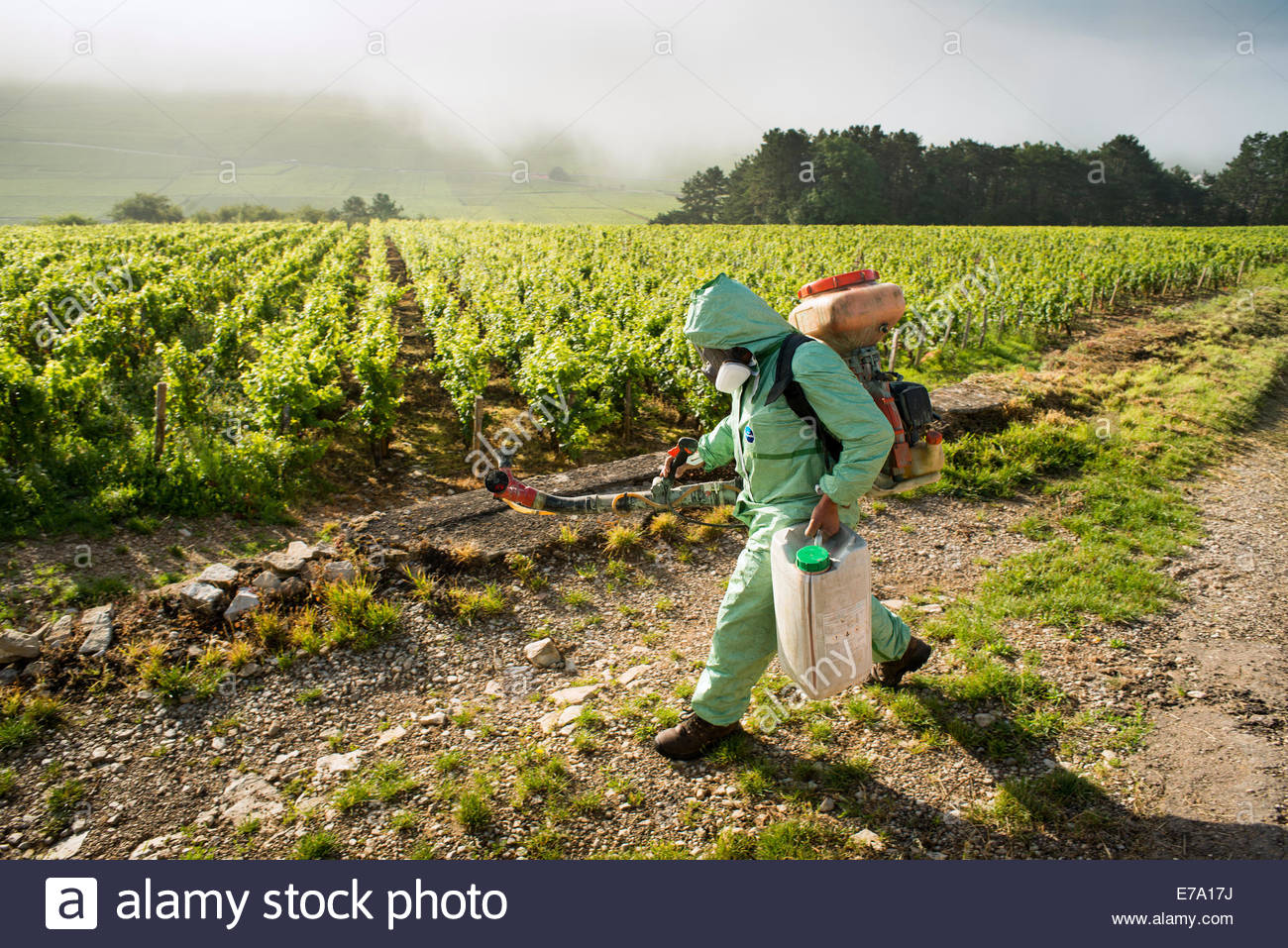

You could read more about safe practices here: https://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/resources/vector385to397.pdf - Spraying at the right time, with the right type of fungicide, applying the right technique. Try to limit fungi developing resistance to fungicides.
- Utilization of Fungi-resistant grape varieties
Fungus-resistant grapes (FRG) are the result of interspecies cross-breeding between V. vinifera and North American and Asian Vitis spp. (i.e. V. riparia, V. amurensis and V. rupestris), which exhibits higher resistance to fungal diseases (Pedneault & Provost, 2016).
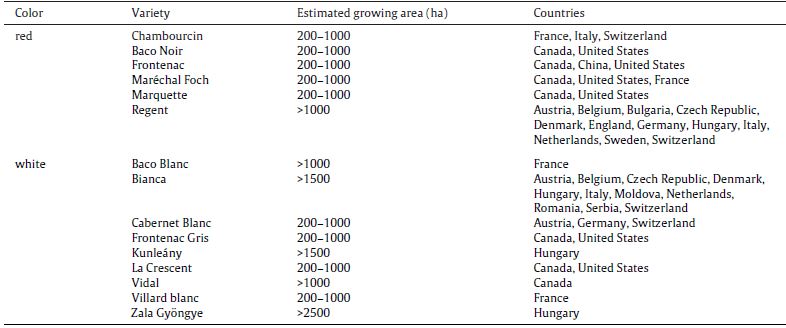
(Fungus resistant varieties (Pedneault & Provost, 2016).
- Official controls of wines in European market
- Specific limits for fungicide and pesticide residues in wine should be legislated. There are suggestions to reduce 10-fold the MLRs in wine, in comparison to established MLRs for grapes (Esteve-Turrillas et al. 2016)
References
Esteve-Turrillas, F. A., Agulló, C., Abad-Somovilla, A., Mercader, J. V., & Abad-Fuentes, A. (2016). Fungicide multiresidue monitoring in international wines by immunoassays. Food chemistry, 196, 1279-1286.
Pedneault, K., & Provost, C. (2016). Fungus resistant grape varieties as a suitable alternative for organic wine production: Benefits, limits, and challenges. Scientia Horticulturae, 208, 57-77. https://www.piwi-international.de/Scientia_Horticulturae_2016_Pedneault.pdf
CONCLUSIONS
Pesticides residues are one of the dangers to watch in the wine industry, especially since there’s no set limit for wine.
Utilization of pesticides should be limited as possible and always following recommended good working practices.
Safety measures should be applied by workers in order to protect their health.
Maximum levels must be set for wine in order to protect public health.
