Globally the consecutive problems regarding agricultural products and food stuffs have driven consumers to loose trust in marketed products, industries, and companies. Thus, globally, in order to ensure food and drink quality, certification of products was introduced.
Videos that refer to food quality and food safety can be found throughout the internet. Below are some links that explains why and how quality certifications are applied.
Currently, only in the EU more than 400 quality assurance and certification schemes are implemented for agriproducts/ foodstuffs/alcoholic beverages.
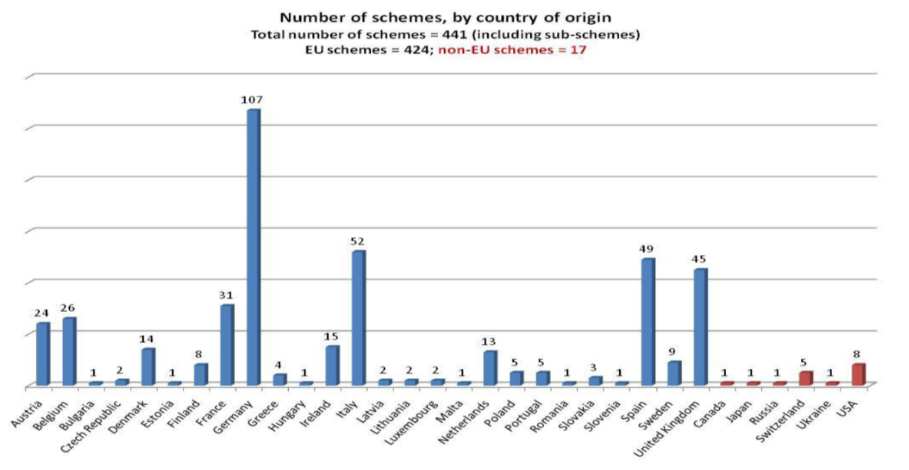
Figure 1. Number of Schemes by country of origin. European Commission, 2016
Among the quality indicators as perceived by consumers, is the geographical indication of a product, i.e., where -location that the product was produced at, with the logical explanation that some areas are “unique” or the “experts” of producing some food or drink or agri-food products.
Geographical Indications (GIs) are considered as intellectual property and are under the Trade Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) agreement (article 22 and article 23 for wines and spirits), which is under the World Trade Organization (WTO).
Specifically, the TRIPS agreement as recorded in the Annex 1C of WTO Agreement covers the furthermost inclusive and up-to-date multilateral agreement on intellectual property incorporating substantive provisions of the Paris Convention (1967), the Berne Convention (1971), the Rome Convention (1961) and the Treaty on IP in Respect of Integrated Circuits (1989).
Precisely, the first effort for International Property Rights took place in Paris in 1883 with the Paris Convention on Intellectual Property, followed by the 1891 Madrid Agreement on indications of source and the 1958 Lisbon Agreement for the Protection of Appellations of Origin.
